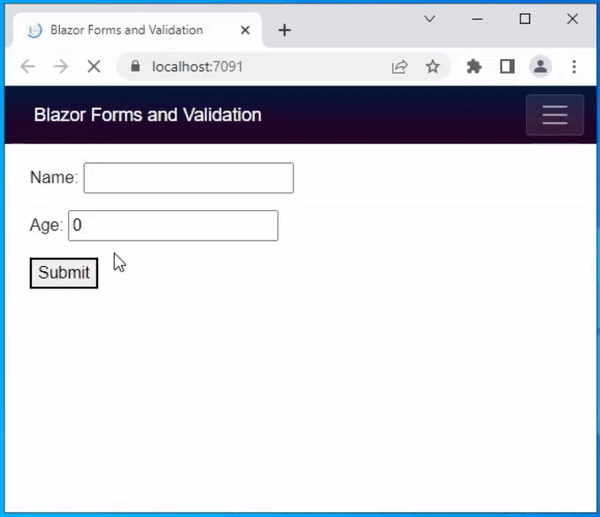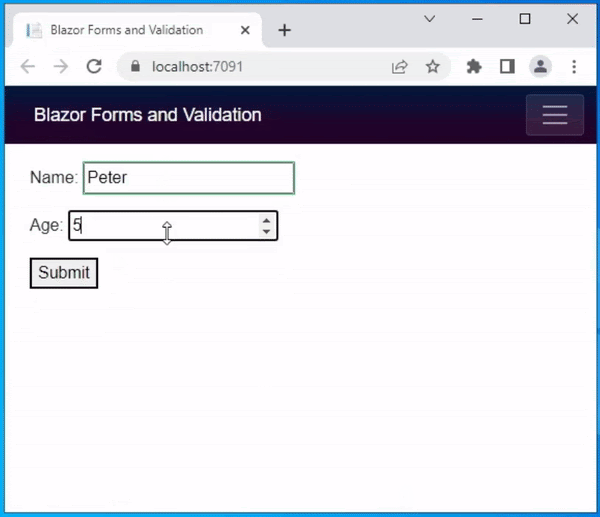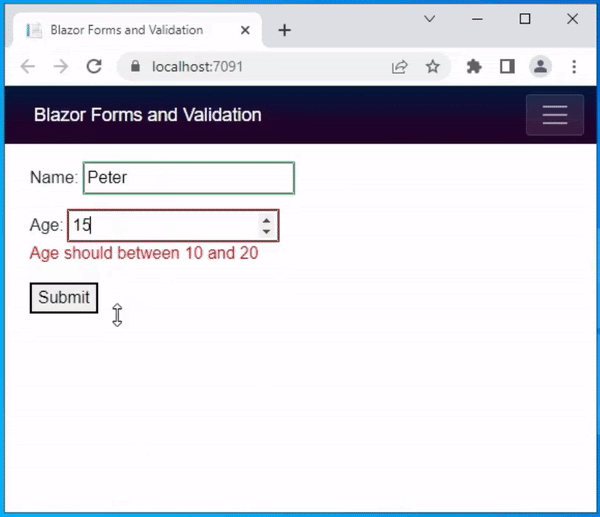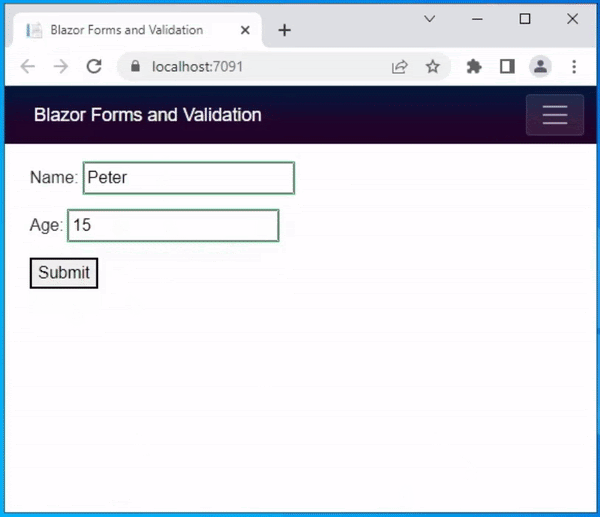
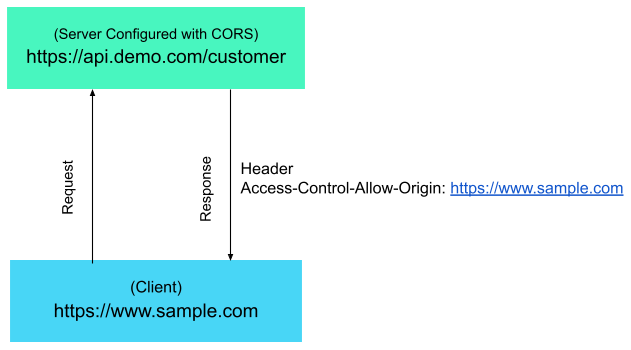
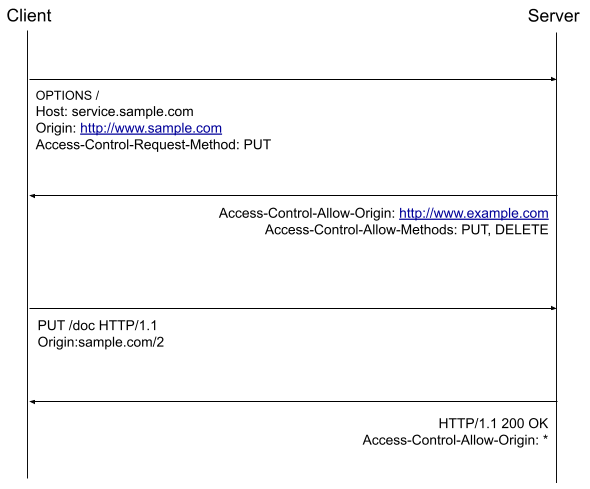
If you’re planning to develop a web application, you might have heard about Vue, React, and Angular. These three are the most popular and widely used frontend frameworks among web developers. Each of these frameworks has its own advantages and disadvantages, and choosing the right one can be a daunting task. In this blog post, we’ll compare Vue, React, and Angular to help you decide which one is the best choice for your project.
Vue.js
Vue.js is a lightweight and progressive JavaScript framework used for building user interfaces. It was created by Evan You in 2014 and has gained popularity because of its simplicity and ease of use. Vue.js is a reactive framework that updates the view automatically when the data changes.
One of the significant advantages of Vue.js is its small size, which makes it an excellent choice for building small to medium-sized applications. Vue.js is also easy to learn, and you can get started with it quickly, even if you’re a beginner. Vue.js has a comprehensive documentation and an active community that provides support and assistance to developers.
Another advantage of Vue.js is its flexibility. You can integrate Vue.js with other libraries and frameworks like React or Angular, which makes it an excellent choice for developing hybrid applications. Vue.js also supports server-side rendering, which improves the performance of web applications.
React
React is a popular JavaScript library for building user interfaces. It was created by Facebook in 2011 and is widely used by large companies like Netflix, Airbnb, and Instagram. React uses a virtual DOM, which improves the performance of web applications by reducing the number of DOM manipulations.
One of the significant advantages of React is its performance. React uses a virtual DOM, which makes it faster than other frameworks like Angular. React also has a large community that provides support and assistance to developers.
React is also flexible and can be used with other libraries and frameworks. You can use React with Vue.js or Angular to develop hybrid applications. React also has a vast ecosystem of third-party libraries and tools that make it easy to develop complex web applications.
Angular
Angular is a popular JavaScript framework for building web applications. It was created by Google in 2010 and is widely used by large companies like Microsoft, IBM, and PayPal. Angular is a full-featured framework that provides everything you need to develop complex web applications.
One of the significant advantages of Angular is its robustness. Angular provides a complete solution for building web applications, including data binding, forms, and routing. Angular also has a large community that provides support and assistance to developers.
Angular also has excellent performance. Angular uses a virtual DOM, which makes it faster than other frameworks like Vue.js. Angular also provides server-side rendering, which improves the performance of web applications.
Vue vs React vs Angular
Now that we’ve looked at the advantages of each framework, let’s compare them to help you decide which one is the best choice for your project.
Learning Curve
When it comes to the learning curve, Vue.js is the easiest to learn. Vue.js has a small API and is straightforward to understand, even if you’re a beginner. React and Angular, on the other hand, have a steeper learning curve. React uses JSX, which can be challenging to learn, and Angular has a lot of concepts that you need to understand before you can start developing web applications.
Performance
When it comes to performance, React and Angular are the clear winners. React uses a virtual DOM, which makes it faster than Vue.js. Angular also uses a virtual DOM and provides server-side rendering, which improves the performance of web applications.
Flexibility
When it comes to flexibility, Vue.js is the clear winner. Vue.js is a lightweight framework that can be easily integrated with other libraries and frameworks. React and Angular are also flexible, but they have a slightly steeper learning curve when it comes to integration with other technologies.
Robustness
When it comes to robustness, Angular is the clear winner. Angular provides a complete solution for building web applications, including data binding, forms, and routing. React and Vue.js are more focused on the view layer and require additional libraries for routing and state management.
Community and Ecosystem
All three frameworks have active communities that provide support and assistance to developers. However, React has the largest ecosystem of third-party libraries and tools. Vue.js also has a vibrant ecosystem, but it is not as large as React’s. Angular also has a large ecosystem, but it is more focused on enterprise applications.
Which one is the best choice for your project?
The answer to this question depends on the specific requirements of your project. If you’re building a small to medium-sized application and want a lightweight and easy-to-learn framework, Vue.js might be the best choice. If you’re building a large application that requires excellent performance and a large ecosystem of third-party libraries, React might be the best choice. If you’re building an enterprise-level application that requires a complete solution for building web applications, including data binding, forms, and routing, Angular might be the best choice.
Conclusion
Vue.js, React, and Angular are all excellent frontend frameworks that have their own advantages and disadvantages. The best choice for your project depends on the specific requirements of your application. Vue.js is a lightweight and easy-to-learn framework that is an excellent choice for small to medium-sized applications. React is a popular and performant framework that has a large ecosystem of third-party libraries and tools. Angular is a robust framework that provides a complete solution for building web applications, including data binding, forms, and routing. Whatever framework you choose, make sure to take the time to learn it properly and follow best practices to ensure the success of your project. For any further information, visit – https://techcedence.com/